Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia / Cardiomyopathy - ARVD / C
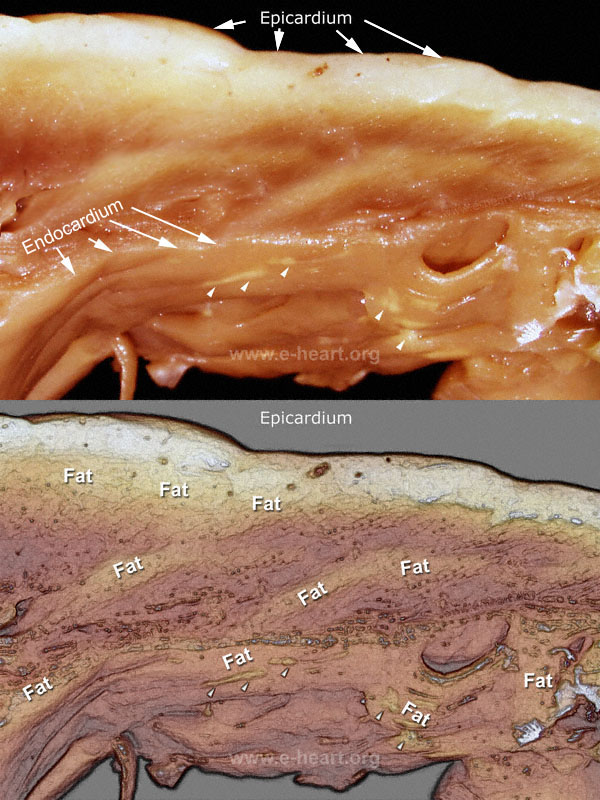 Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/cardiomyopathy (ARVD/C) is characterized by segmental and progressive fibrofatty replacement of the right ventricular myocardium associated with ventricular tachycardia, syncope and sudden death. Involvement of the left ventricle is seen in some patients with relative sparing of the interventricular septum. The prevalence varies between 1 in 1000 to 1 in 5000 individuals. Patients usually present in their second to fifth decades. ARVD/C is increasingly recognized as an important cause of sudden cardiac death; it accounts for 20% of sudden death in young adults and 25% of sudden death among athletes in the Italian population.
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/cardiomyopathy (ARVD/C) is characterized by segmental and progressive fibrofatty replacement of the right ventricular myocardium associated with ventricular tachycardia, syncope and sudden death. Involvement of the left ventricle is seen in some patients with relative sparing of the interventricular septum. The prevalence varies between 1 in 1000 to 1 in 5000 individuals. Patients usually present in their second to fifth decades. ARVD/C is increasingly recognized as an important cause of sudden cardiac death; it accounts for 20% of sudden death in young adults and 25% of sudden death among athletes in the Italian population.
 Familial occurrence of ARVD/C has an estimated range between 30% to 80% with predominantly autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance and incomplete penetrance. To date, there are 11 genomic loci associated with different genetic variants of ARVD/C identified largely through linkage analysis. Five of these loci were found to harbor genes encoding desmosomal proteins that include plakoglobin (JUP), desmoplakin (DSP), plakophilin-2 (PKP2), desmoglein-2 (DSG2) and desmocollin-2 (DSC2). Data show that at least 40% of ARVD/C probands harbor a mutation in one of these desmosomal proteins. PKP2 appears to be the most commonly involved gene in both Dutch and US cohorts.
Familial occurrence of ARVD/C has an estimated range between 30% to 80% with predominantly autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance and incomplete penetrance. To date, there are 11 genomic loci associated with different genetic variants of ARVD/C identified largely through linkage analysis. Five of these loci were found to harbor genes encoding desmosomal proteins that include plakoglobin (JUP), desmoplakin (DSP), plakophilin-2 (PKP2), desmoglein-2 (DSG2) and desmocollin-2 (DSC2). Data show that at least 40% of ARVD/C probands harbor a mutation in one of these desmosomal proteins. PKP2 appears to be the most commonly involved gene in both Dutch and US cohorts.

