Molecular Anatomy of the Heart (IV)
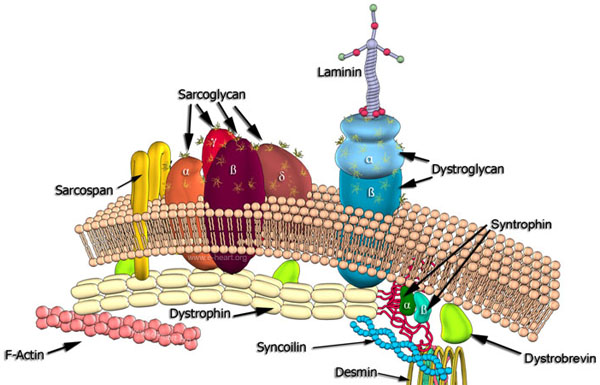
Dystrophin-associated protein complex (DAPC). Multiple proteins form a scaffold that links the cellular cytoskeleton to the extracellular matrix. This large multimeric complex is composed of transmembrane proteins dystroglycan, sarcoglycans and sarcospan and intracellular component of dystrobrevin and syntrophin which interacts with the C-terminal domain of dystrophin. In the sarcoplasmic domain, the N-terminal of dystrophin binds to F-actin. The intermediate filaments of the sarcoplasm (desmin) also interact with DAPC. Dystroglycan has two subunits. One traverses the sarcolemma (ß-subunit) and the other subunit (α) works as a receptor for laminin-2 in the extracellular space. The sarcoglycans are glycosylated transmembrane proteins which may play a role in stabilizing the DAPC.
Another very specialized structure in the sarcolemma is the intercalated disc wich contains subspecialized zones including nexuses or gap juntions, and desmosomes.

